Making hydrogen easily and cheaply is a dream goal for clean, sustainable energy. Bacteria have been doing exactly that for billions of years, and now chemists at the University of California, Davis, and Stanford University are revealing how they do it, and perhaps opening ways to imitate them.
A study published Oct. 25 in the journal Science describes a key step in assembling the hydrogen-generating catalyst.
"It's pretty interesting that bacteria can do this," said David Britt, professor of chemistry at UC Davis and co-author on the paper. "We want to know how nature builds these catalysts — from a chemist's perspective, these are really strange things."
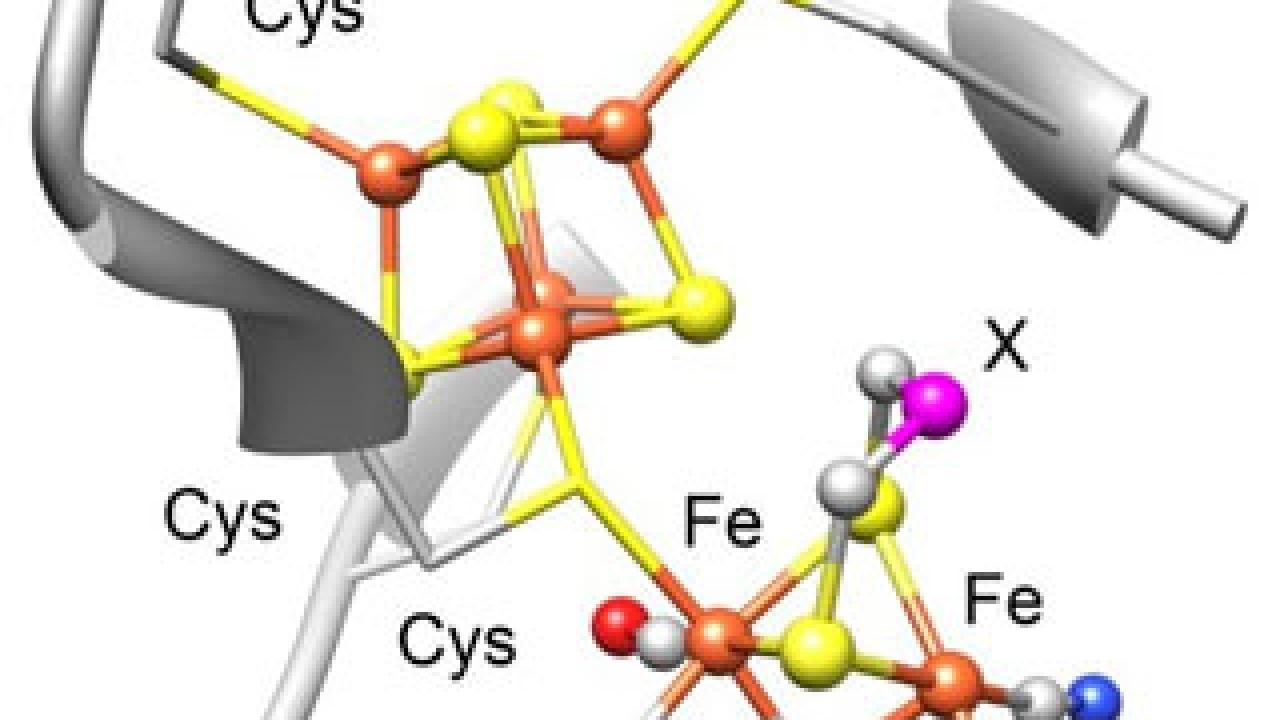
The bacterial catalysts are based on precisely organized clusters of iron and sulfur atoms, with side groups of cyanide and carbon monoxide. Those molecules are highly toxic unless properly controlled, Britt noted.
The cyanide and carbon monoxide groups were known to come from the amino acid tyrosine, Britt said. Jon Kuchenreuther, a postdoctoral researcher in Britt's laboratory, used a technique called electron paramagnetic resonance to study the structure of the intermediate steps.
They found a series of chemical reactions involving a type of highly reactive enzyme called a radical SAM enzyme. The tyrosine is attached to a cluster of four iron atoms and four sulfur atoms, then cut loose leaving the cyanide and carbon monoxide groups behind.
"People think of radicals as dangerous, but this enzyme directs the radical chemistry, along with the production of normally poisonous CO and CN, along safe and productive pathways," Britt said.
Kuchenreuther, Britt and colleagues also used another technique, Fourier Transform Infrared to study how the iron-cyanide-carbon monoxide complex is formed. That work will be published separately.
"Together, these results show how to make this interesting two-cluster enzyme," Britt said. "This is unique, new chemistry."
Britt's laboratory houses the California Electron Paramagnetic Resonance center (CalEPR), the largest center of its kind on the west coast.
Other authors on the paper are: at UC Davis, postdoctoral researchers William Myers and Troy Stich, project scientist Simon George and graduate student Yaser NejatyJahromy; and at Stanford University, James Swartz, professor of chemical engineering and bioengineering. The work was supported by grants from the U.S. Department of Energy.
Media Resources
Andy Fell, Research news (emphasis: biological and physical sciences, and engineering), 530-752-4533, ahfell@ucdavis.edu
David Britt, UC Davis Department of Chemistry, (530) 752-6377, rdbritt@ucdavis.edu